Webb Captures Rarest Cosmic Explosion, Revealing Origin of Heavy Elements
Introduction
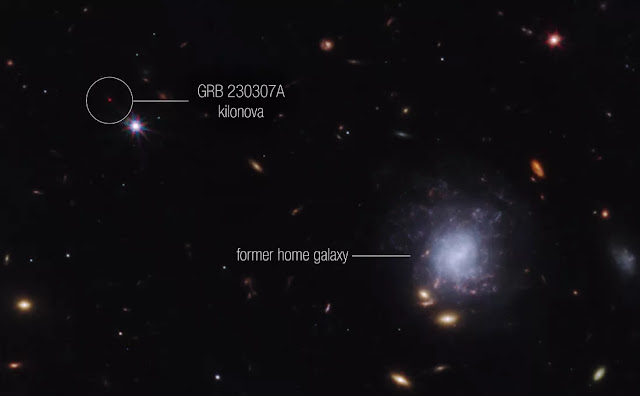
On March 7, 2023, NASA's James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) detected an extremely rare kilonova explosion. A kilonova is a cataclysmic event that occurs when two neutron stars merge. Neutron stars are the incredibly dense cores of massive stars that have exploded as supernovae. When two neutron stars merge, they create a short-lived, but extremely bright explosion that spews out heavy elements like gold and platinum.
The kilonova that JWST detected, dubbed GRB 230307A, was the second brightest gamma-ray burst ever recorded. It was so bright that it was visible to telescopes on Earth even though it occurred 1 million light-years away.
What is a kilonova?
A kilonova is a type of supernova that occurs when two neutron stars merge. Neutron stars are incredibly dense objects, with a mass about 1.4 times that of the Sun, but compressed into a sphere about the size of a city. When two neutron stars merge, they create a short-lived, but extremely bright explosion that releases a tremendous amount of energy.
How did JWST detect GRB 230307A?
JWST is equipped with a suite of infrared instruments that allow it to see objects that are too faint or too distant to be seen by visible light telescopes. This makes JWST ideal for studying kilonovae, which are typically very faint and occur in distant galaxies.
JWST detected GRB 230307A as part of a survey for gamma-ray bursts. Gamma-ray bursts are the most energetic explosions in the universe, and they are thought to be caused by a variety of events, including the collapse of massive stars and the mergers of neutron stars.
What did JWST learn about GRB 230307A?
JWST's infrared capabilities allowed scientists to study GRB 230307A in unprecedented detail. They were able to identify the home address of the two neutron stars that created the kilonova, and they also detected the presence of heavy elements like tellurium and lanthanides.
What does this discovery mean?
The discovery of GRB 230307A by JWST is a significant scientific breakthrough. It provides new insights into the formation of heavy elements in the universe and the physics of kilonovae. It also demonstrates the power of JWST to study distant and faint astronomical objects.
Conclusion
The discovery of GRB 230307A by JWST is a major step forward in our understanding of kilonovae and their role in the evolution of the universe. JWST's infrared capabilities allowed scientists to study this event in unprecedented detail, and the data they collected is already providing new insights into the physics of these events and the formation of heavy elements.
This discovery is also a testament to the power of JWST, which is the most powerful telescope ever built. JWST is able to see objects that are too faint or too distant to be seen by other telescopes, and it is already revolutionizing our understanding of the universe.





0 Comments